
Process control systems are present in almost all modern automated and engineering systems. These systems are key to increasing productivity, maintaining quality, and improving safety.
Learning Objectives
- Define a process
- Define a control
- List categories of processes
- Define an open-loop control system
- Define a closed-loop control system
- Identify the advantages of using process control
Language: English
Estimated Time (Hrs.): 1.1
Micro-module: No
Micro-module Series: No

Process control systems are used in processes as simple as filling a tank with liquid and as complex as chemical engineering. However, the fundamentals and terminology are consistent for all control systems.
Learning Objectives
- Identify the basic components of manual and automatic control systems
- Identify the signal types in an automatic control system
- List the advantages of a manual control system
- List the advantages of an automatic control system
- List factors that cause errors in a process control system
Language: English
Estimated Time (Hrs.): 1.7
Micro-module: No
Micro-module Series: No
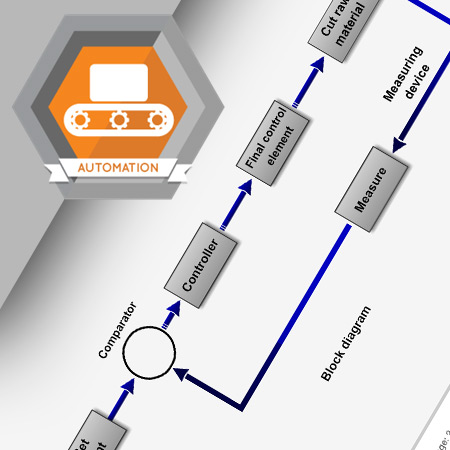
Two key components of an automated process control system are the set point and the comparator. The set point device establishes a value for the desired state. The comparator device calculates how far the process is from this value.
Learning Objectives
- List examples of set point devices
- Define an op-amp device
- List the functions that a comparator performs on feedback and input signals
- Understand how an error signal is produced in a differential amplifier
Language: English
Estimated Time (Hrs.): 1
Micro-module: No
Micro-module Series: No

Keeping modern industrial automated systems under control can require high-level calculations and decisions. The controller is the component in a feedback loop that makes the calculations and decisions.
Learning Objectives
- Identify the purpose of the controller in an automatic control system
- Understand the differences between proportional, integral, and derivative controls
- Identify the major types of PID controllers
- Define loop tuning
- Identify the major methods of loop tuning
Language: English
Estimated Time (Hrs.): 1.5
Micro-module: No
Micro-module Series: No

Industrial processes often require the control of several variables to achieve the desired state of a finished product. This course will discuss controlling these multivariate processes.
Learning Objectives
- Define a multivariate process
- Identify the key features of a multivariate process
- Identify applications of multivariate process controls
- Understand the terms coupling and decoupling
Language: English
Estimated Time (Hrs.): 1.2
Micro-module: No
Micro-module Series: No
